Factors Affecting Weight & Health Q&A
Understanding the factors that affect weight and health is essential for making informed decisions about your well-being. These factors can include genetics, metabolic rate, diet, physical activity levels, hormonal imbalances, and environmental influences. At Cape Fear Physical Medicine and Rehab, we provide personalized guidance to help you navigate these elements, offering tailored solutions to improve both your weight and overall health. Our professional team is dedicated to supporting you in achieving long-term health goals through comprehensive care and lifestyle adjustments. For more information, contact us today or schedule an appointment online. We are conveniently located at 1540 Purdue Dr, Ste. 200, in Fayetteville, NC 28303.
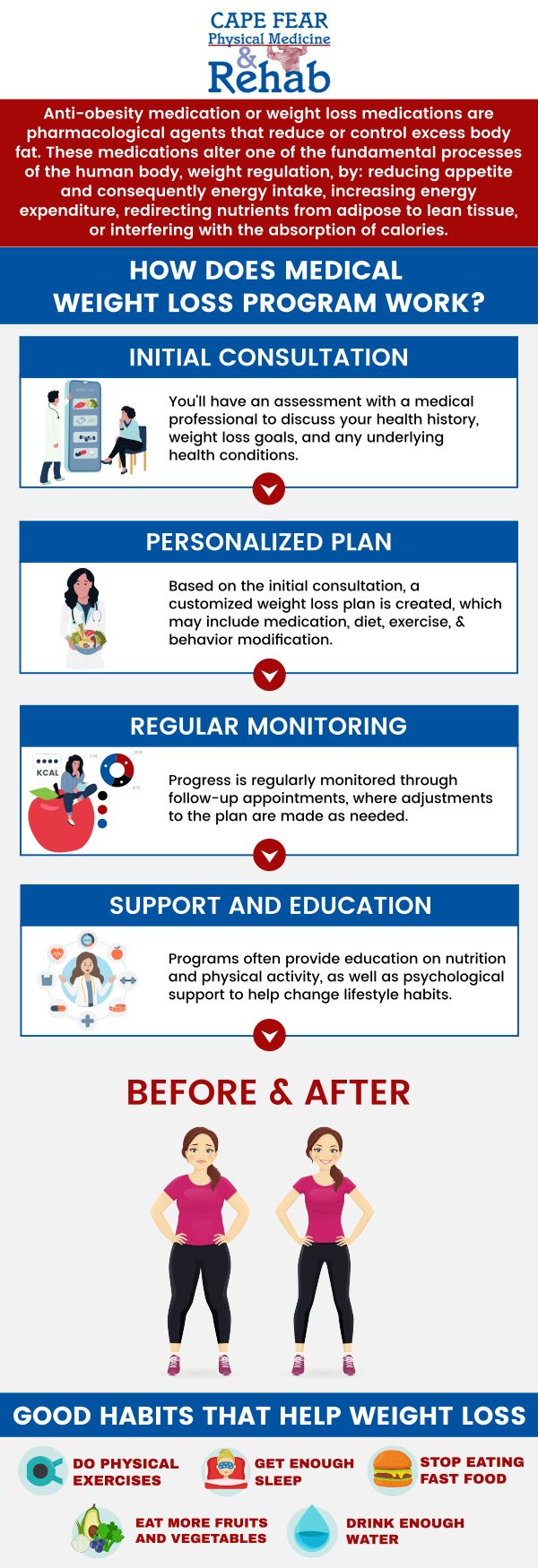
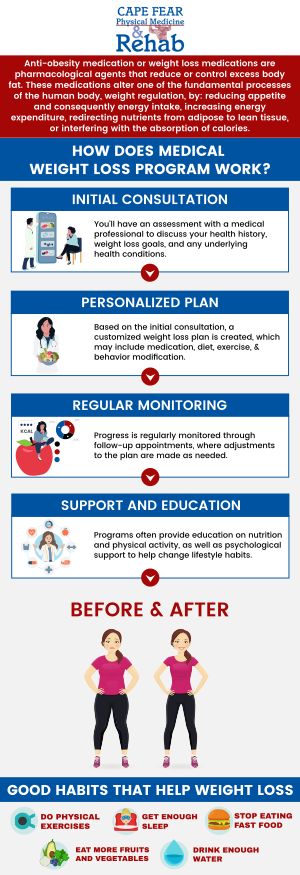


Table of Contents:
What are some causes of weight gain?
What foods cause weight gain?
Why are you gaining weight for no reason?
How do you reset your metabolism?
Numerous factors can contribute to weight gain, including:
Inactive lifestyle – Being inactive can slow your metabolism and lead to weight gain.
Overeating – Taking in more calories than your body requires can result in weight gain.
Medical history – Weight gain is a potential side effect of certain medical conditions, including hypothyroidism and polycystic ovary syndrome.
Hormonal changes – Weight gain can be caused by hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, and menopause.
Medication – Weight gain has been reported as a side effect of certain medications such as corticosteroids, antipsychotics, and antidepressants.
Stress – Excessive stress can raise cortisol levels, which can cause weight gain.
Genetics – Your genes affect how your body processes food.
Age – As you get older, your metabolism slows down, which makes gaining weight easier.
Alcohol consumption – Drinking alcohol can significantly increase your calorie intake and affect your judgement, which makes it easier to overeat.
Lack of sleep – Sleep deprivation can interfere with the hormones that control appetite and hunger, causing weight gain.
Weight gain commonly results from over-consumption of calories. Food categories that are frequently linked to weight gain include:
High-fat foods – Foods with high amounts of unhealthy fats, such as butter, cheese, and fatty meats, can cause weight gain when consumed in large quantities.
Fried foods – Fried foods often contain large amounts of calories, bad fats, and cholesterol. Regular consumption of fried and deep-fried meals is commonly linked to weight gain and can negatively impact cholesterol levels. This can increase the risk of heart disease and other health issues if consumed frequently.
Sugary drinks – Sweet beverages, such as soda, juice, and sports drinks, can significantly increase the calorie count in your diet and cause weight gain.
Foods with refined carbohydrates – Products made with white flour such as white bread, pasta, and baked goods are usually high in calories and low in fiber. If consumed in excess, these foods can lead to weight gain.
Processed foods – Processed foods often have high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and calories. These components can cause weight gain if consumed in excess.
There are many potential causes of unexplained weight gain. Overeating is among the most common causes of unexplained weight gain. This may occur if you don’t monitor your portion sizes, snack frequently, or eat high-calorie foods often.
Hormonal changes can also cause unexplained weight gain. These changes can occur during puberty, pregnancy, menopause, or the menstrual cycle. High levels of stress can also lead to weight gain, as stress can increase cortisol levels.
Living an inactive lifestyle is another common cause of unexplained weight gain. Your metabolism will slow down if you don’t exercise enough. This is common for people who work a desk job, spend a lot of time sitting or lying down, or don’t have a regular fitness regimen.
If you’re experiencing unexplained weight gain, it’s important to talk to a healthcare provider to rule out any underlying medical conditions or medication side effects. Our weight loss facilities can help you determine the root cause of your weight gain and prescribe effective treatment.
You can do a variety of things to increase your metabolism and burn calories more effectively, including:
Strength exercises – The more muscle you have, the more calories your body can burn. You can develop and maintain muscle mass by doing strength exercises.
Eat enough protein – Eating high-protein foods can help you feel full longer and speed up your metabolism.
Avoid skipping meals – Skipping meals can slow down your metabolism and lead to overeating later in the day. Try to eat small, frequent meals throughout the day to keep your metabolism healthy.
Improve hydration – Staying hydrated is important for maintaining a healthy metabolism. Aim for eight glasses or more of water each day.
Get enough sleep – Lack of sleep can interfere with the hormones that regulate your metabolism and appetite. Aim to sleep for at least 7 to 8 hours every night.
Be consistent – Consistency is key to maintaining a healthy metabolism. Stick to a proper diet and exercise routine to keep your metabolism performing at its best.
At Cape Fear Physical Medicine and Rehab, we are committed to helping you achieve your health and weight management goals. Our professional team provides personalized care and support to ensure lasting results. Contact us today or schedule an appointment to learn more about how we can assist you in improving your overall well-being. We are conveniently located at 1540 Purdue Dr, Ste. 200, in Fayetteville, NC 28303. We serve patients from Fayetteville NC, Woodfield NC, Hope Mills NC, Fort Bragg NC, Eastover NC, and surrounding areas.

Check Out Our 5 Star Reviews


Additional Services You May Like
▸ Weight Loss & Wellness Program
▸ Botox for Migraine
▸ EMG Nerve Conduction Studies
▸ Epidural Steroid Injections
▸ Radiofrequency Ablation
▸ Rehabilitation Consultations
▸ Facet Injections
▸ Sacroiliac Joint Injections
▸ Joint Injections
▸ Genicular Nerve Blocks
▸ Prosthetic Evaluation/Management
▸ Adjuvant Therapy/Care
▸ Spasticity Management
▸ Stroke Treatment
▸ Multiple Sclerosis
▸ Spinal Cord Injury
▸ Traumatic Brain Injury
▸ Lifestyle Medicine
▸ Phentermine
▸ Qsymia
▸ Contrave

Additional Services You May Like
▸ Weight Loss & Wellness Program
▸ Botox for Migraine
▸ EMG Nerve Conduction Studies
▸ Epidural Steroid Injections
▸ Radiofrequency Ablation
▸ Rehabilitation Consultations
▸ Facet Injections
▸ Sacroiliac Joint Injections
▸ Joint Injections
▸ Genicular Nerve Blocks
▸ Prosthetic Evaluation/Management
▸ Adjuvant Therapy/Care
▸ Spasticity Management
▸ Stroke Treatment
▸ Multiple Sclerosis
▸ Spinal Cord Injury
▸ Traumatic Brain Injury
▸ Lifestyle Medicine
▸ Phentermine
▸ Qsymia
▸ Contrave